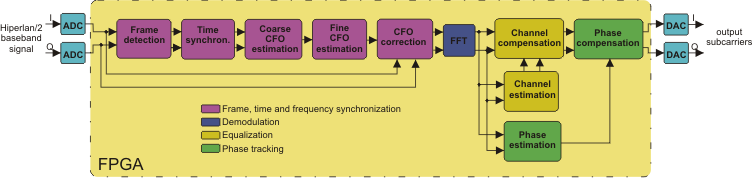
This is a hardware demonstrator of a Wi-Fi 802.11a/g receiver. It includes frame detection, time and frequency synchronization, demodulation, channel estimation, equalization and phase tracking.
Wi-Fi 802.11a/g receiver characteristics:
- Based on ODFM transmission (baseband signal built using a 64-point FFT)
- Modulation types from BPSK to 64-QAM (data rates from 6 to 54 Mbps)
- Sampling frequency: 20 MHz
- Symbol duration: 4 μs (80 samples)
- Data transmitted in bursts, always preceded by a preamble which is used for synchronization and channel estimation
Wi-Fi 802.11a/g receiver scheme
Fixed-point and floating-point receiver models comparison
(multipath channel with an rms delay spread 50ns, SNR = 30dB)
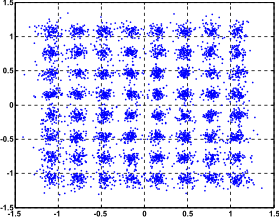
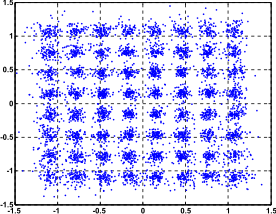
Receiver Performance:
(multipath channel with an rms delay spread 50ns)
- Frame detector:
- Detection failure probability (PDF): PDF < 0.3% for SNR = 6dB and PDF = 0.1% for SNR > 6dB.
- False alarm probability (PFA): PFA < 0.1% for SNR ≥ 6dB.
- Time synchronization: deviation -4 ~ 0 samples by 99.8% of the received frames and SNR = 6dB, nearly 100% for SNR > 6dB.
- Frequency synchronization: residual carrier frequency offset (CFO) of 900Hz for SNR ≥ 20dB.
- Resources on Virtex-II FPGA: 2986 slices, 20 embedded multipliers and 8 DPRAM
- Consumption: preamble search stage 181.56 mW and processing stage 260.65 mW.
- PER degradation for 64-QAM at PER = 10-2: 0.45dB (0.25dB due to receiver quantification and 0.2 due to synchronization errors).
PER comparison
(blue: fixed-point receiver and real synchronization, red: floating-point and ideal synchr.)

Prototype implemented on development kit Xtreme DSP:
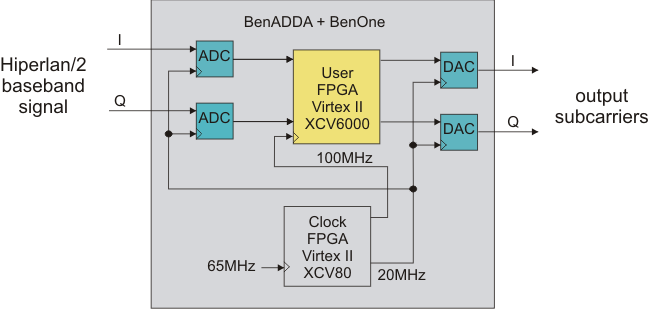

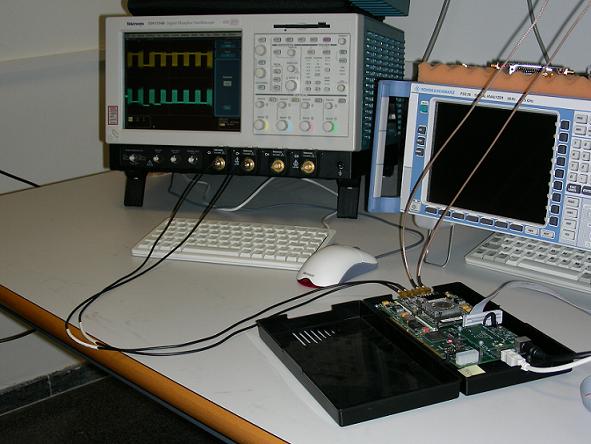
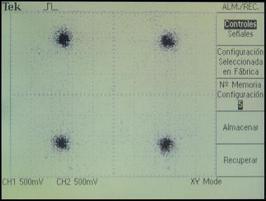
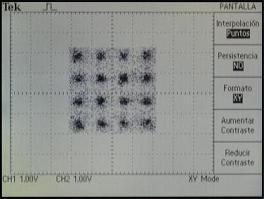
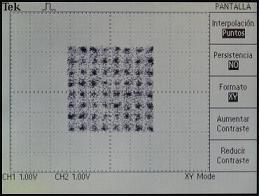
Output constellations